Welcome to your comprehensive guide to international shipping terms! Navigating the intricate world of international shipping customs can often feel like learning a foreign language. With a myriad of complex terms and regulations, it can be hard to understand. But don’t worry! We’re here to help.
Whether you’re an experienced e-commerce manager or budding online merchant, mastering the language of international shipping can help you conduct international transactions seamlessly.
We’ve compiled the essential international shipping terminology you need to demystify the customs process and navigate the complexities of global shipping.
Looking to understand import duties, decode Harmonized System (HS) codes, or mitigate the risk of customs compliance? You’ll find all your answers in our glossary for international shipping terms! This glossary is the ultimate resource for e-commerce professionals that are ready to expand their global reach and streamline their international shipping operations.
So, let’s dive in and explore the world of international shipping terms together!

International Shipping Glossary
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
A
B
Bonded Warehouse
A facility where imported goods can be stored without paying customs duties until they are cleared for release.
C
Certificate of Origin
A Certificate of Origin (CO) is a document issued by an authorized organization or chamber of commerce that certifies the origin of goods being exported from one country to another. It serves as evidence to verify the country where the goods were produced, manufactured, or processed.
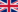
CN22
A customs declaration form containing information about the content of a shipment. The CN22 form can be used when the order value is less than €425 or £270 and weighs less than 2 kg. CN22 forms can only be used with postal carriers.
Ready to learn how to fill out a CN22 form? We’ve got a great blog for you! It’s all about CN22 and CN23 Customs Declarations for International Shipping.
CN23
A customs declaration form containing information about the content of a shipment. The CN23 form can be used when the order value is more than €425 or £270 and weighs above 2 kg. The CN23 form is similar to the CN22, but it contains more details. CN23 forms can only be used with postal carriers.
Commercial Invoice
When shipping across international borders, there is no way around one of the most commonly used international shipping terms ‘Commercial Invoice’. A Commercial Invoice is a legal document required for any commercial shipment to a country outside the European Union (or islands within EU). The commercial invoice contains information about the contents of a shipment and states who pays for import duties.
Are you wondering what the main differences are between a commercial invoice and a CN22 or CN23? Our comprehensive blog on commercial invoices provides a detailed overview of these and other key differences. Additionally, our Customs Declaration Generator offers a free tool for creating commercial invoices in a few simple steps.
CP71
A CP71 is a shipping note commonly used in international shipping. It is required when including a CN23 customs declaration form with a shipment. This note provides additional details about the contents of the package and helps facilitate customs clearance processes at the destination country.
Customs
As a governmental authority, customs oversees the regulation and control of the flow of goods across international borders. Their responsibilities include enforcing trade laws and regulations, collecting duties and taxes, conducting inspections, and ensuring compliance with import and export requirements. By facilitating the movement of goods while safeguarding national interests, customs are a vital part of international trade and commerce.
Customs Clearance
Customs clearance is the formal procedure conducted by customs authorities to validate and approve the import or export of goods across international borders. This process involves submitting the necessary paperwork, such as invoices and permits, providing accurate information about the goods being shipped, paying any applicable taxes or duties, and adhering to specific regulatory requirements set by the importing or exporting country. Customs clearance ensures compliance with trade laws and regulations, facilitates the smooth movement of goods, and helps prevent delays or complications in the import/export process.
Customs Clearance
Customs clearance is the formal procedure conducted by customs authorities to validate and approve the import or export of goods across international borders. This process involves submitting the necessary paperwork, such as invoices and permits, providing accurate information about the goods being shipped, paying any applicable taxes or duties, and adhering to specific regulatory requirements set by the importing or exporting country. Customs clearance ensures compliance with trade laws and regulations, facilitates the smooth movement of goods, and helps prevent delays or complications in the import/export process.
Customs Broker
A licensed professional who facilitates the clearance of goods through customs.
Customs Audit
A customs audit is an examination of a company’s import and export activities by customs authorities to ensure compliance with regulations.
Customs Declaration
A document in which the sender provides information about the contents, value, and origin of goods being imported or exported. A customs declaration can be a specific part of the customs form or a separate document.
See also CN22, CN23 and Commercial Invoice.
Customs Form
A customs form is a document used by customs authorities to record information about goods being imported or exported. It typically includes details such as the sender’s and recipient’s information, the nature of the goods, their quantity, value, and sometimes their intended use.
D
DAP Incoterm
DAP (Delivered At Place) is an Incoterm where the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to a named place agreed upon with the buyer, typically at the destination country. Under DAP terms, the seller bears all risks and costs associated with delivering the goods to the agreed-upon destination, including transportation, customs clearance for export, and loading/unloading charges. However, the buyer is responsible for customs clearance upon arrival in the destination country, including paying any applicable duties, taxes, and customs fees.
DDP Incoterm
DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) is an Incoterm used in international trade contracts, indicating that the seller is responsible for delivering the goods to the buyer’s specified destination, including bearing all costs and risks associated with customs clearance for import. Under DDP terms, the seller covers all charges, surcharges, and duties for customs clearance in the destination country, ensuring that the goods are delivered to the buyer’s premises ready for unloading.
Dutiable Value
The declared value of goods for customs purposes, used to calculate duties and taxes.
E
EAN
EAN stands for European Article Number. It was introduced by the predecessor institution of today’s GS1 with the aim of providing all European products with individual article numbers. In 2009 the EAN was replaced by the 13-digit Global Trade Item Number (GTIN).
EORI number
EORI stands for “Economic Operators Registration and Identification number.” It is a unique identifier used for registering and tracking customs information in trade with non-EU countries. This number allows for faster exchange of information with customs authorities outside the EU.
EUCU
EUCU is the abbreviation for the European Union Customs Union. The EUCU is a customs union comprising the member states of the European Union (EU). It facilitates trade between its members by removing customs duties (tariffs) and implementing a common external tariff on goods imported from non-member countries. This means that once goods have cleared customs in one EU member state, they can be shipped to other member states without further tariffs or customs checks.
Excise Duty
A tax on specific goods produced domestically that are considered to be socially or environmentally harmful, such as alcohol, tobacco, fuel, and certain luxury items.
Exporter of Record
The exporter of record (EOR) refers to the entity or individual who is officially recognized as the party responsible for exporting goods from one country to another. This designation carries legal and regulatory implications, as the exporter of record is required to comply with all export laws, regulations, and documentation requirements of the exporting country.
The exporter of record may be the actual manufacturer or seller of the goods, an authorized agent acting on behalf of the manufacturer or seller, or another party involved in the export transaction.
Export License
Permission granted by the exporting country’s government to export certain goods.
F
Free Trade Agreement (FTA)
An agreement between two or more countries to reduce or eliminate tariffs and other barriers to trade.
G
GTIN
GTIN stands for Global Trade Item Number. They are unique identifiers assigned to products by the manufacturer, and they help ensure that products are accurately identified, tracked, and managed throughout the global supply chain.
The GTIN is typically encoded into a barcode that can be scanned electronically.
There are several different types of GTINs, depending on the level of specificity required.
H
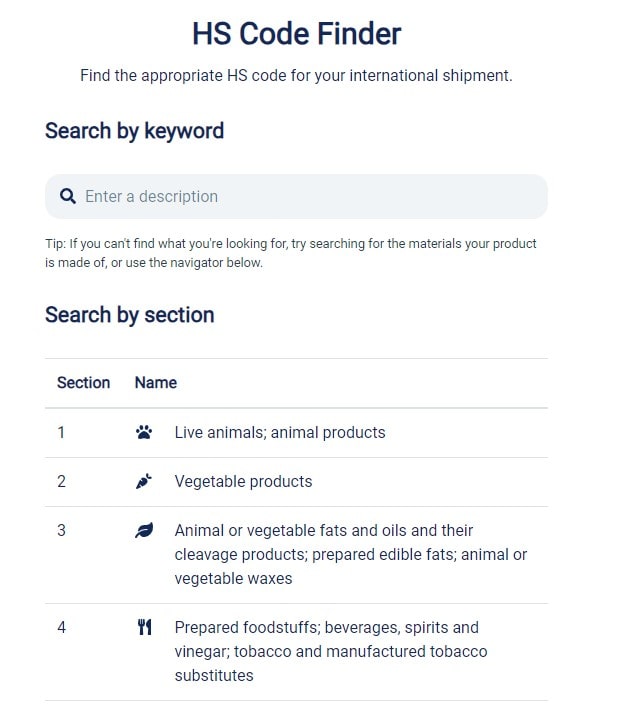
Harmonized System (HS) Code
The HS code is one of the most frequently used international shipping terms and stands for Harmonized System Code. It is an internationally standardized system of names and numbers used to classify traded products for customs purposes. The Harmonized System was developed and is maintained by the World Customs Organization.
Each product is assigned a unique HS code based on its nature, composition, and intended use. HS codes consist of a series of digits arranged in a hierarchical structure. The first six digits represent the general category of the product, while additional digits provide more detailed classification.
Want to learn more? We’ve got you! Check out our HS Code Guide for Online Retailers.
And since we know that looking up the code can be difficult, we’ve created this handy HS Code Finder so you can find the right code for your products quickly and easily.
I
Importer of Record
The importer of record (IOR) is the individual or entity officially recognized as responsible for bringing goods into a country from abroad. This designation holds legal and regulatory significance, as the importer of record is obligated to comply with all import laws, regulations, and documentation requirements of the importing country.
The importer of record may be the buyer or consignee of the goods, the owner or importer of record’s designated agent, or another party involved in the import transaction.
Import Duty
Import duty, also known as customs duty or tariff, is a tax imposed by a government on goods imported into a country from abroad. Import duties are typically levied as a percentage of the value of the imported goods or based on specific quantities or units, depending on the classification of the goods and the tariff schedule of the importing country.
Import License
A legal document by the importing country’s government that grants permission to import certain goods.
Import Quota
A government-imposed limit on the quantity of a particular product that can be imported into a country during a specified period. Import quotas are often used to shield domestic industries from foreign competition by limiting the amount of imported goods that can enter the country.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of 11 internationally recognized rules which define the responsibilities and obligations of sellers and buyers in international shipping. They specify who is responsible for paying for and managing the shipment, insurance, documentation, customs clearance, and other logistical activities.
We know that Incoterms are one of the most complicated international shipping terms. That’s why we’ve created this Incoterms guide, where you can see all Incoterms and obligations in one overview.
International Shipping
International shipping refers to the process of sending a parcel from one country to another. While it might sound straightforward, it involves navigating a complex web of international laws, rules, and regulations that govern global trade. Unlike domestic shipping, which is governed by local legislation, international shipping is subject to a myriad of legal frameworks that can vary significantly from one country to another.
The challenges of international shipping are compounded when sending parcels outside of shared economic areas, as demonstrated by the complexities arising from events like Brexit. Companies engaging in international shipping, particularly to regions such as APAC, North America, and South America, must contend with varied customs regulations and shipping controls, which can pose significant logistical hurdles.
Successfully navigating international shipping requires more than just understanding international shipping terms and how to fill out forms. It requires finding the right partner and developing a targeted strategy tailored to the specific needs of each destination market. By understanding and adhering to international laws and regulations, companies can mitigate risks, minimize delays, and ensure the smooth transit of goods across borders, ultimately facilitating global trade and commerce.
Whether you’re considering shipping internationally or your business is looking to boost global sales, our complete guide to international shipping can help you nail it from day one.
Or download our practical International Shipping Roadmap here for free!
International Shipping Carrier
An International Shipping Carrier is a company that specializes in transporting goods across international borders, providing services such as packaging, customs clearance, and delivery to the final destination. International shipping carriers offer various modes of transportation, such as air freight, ocean freight, road freight, and rail freight, depending on the nature of the goods and the specific requirements of the shipment.
Examples of well-known international shipping carriers include FedEx, UPS, DHL, Maersk Line, and CMA CGM. These companies have extensive networks, infrastructure, and expertise to manage the complexities of international trade and ensure the timely and secure delivery of goods worldwide.
Choosing the right international shipping carrier is crucial for businesses engaged in international trade, as it can impact factors such as shipping costs, transit times, reliability, and customer satisfaction.

International Shipping Strategies
International shipping strategies are comprehensive plans developed by businesses to efficiently and effectively manage the transportation of goods across international borders.
These strategies encompass various aspects such as selecting the appropriate shipping methods, optimizing supply chain routes, minimizing costs, navigating customs regulations, ensuring compliance with international trade laws, and enhancing customer satisfaction. International shipping strategies are tailored to the specific needs and goals of each business and are continuously refined to adapt to changing market conditions and regulatory environments.
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Prohibited Goods
Items that are not allowed to be imported or exported under any circumstances due to legal, safety, security, environmental, or other regulatory reasons. These goods are subject to restrictions imposed by customs authorities, international agreements, or domestic laws of the importing or exporting countries. Common examples of prohibited goods in international shipping include illegal drugs, weapons and firearms, hazardous materials and endangered species.
Q
R
Restricted Goods
Restricted goods in international shipping refer to items that are subject to certain limitations, regulations, or requirements when being transported across international borders. While these goods are not strictly prohibited from shipping, they may require special permits, licenses, or compliance with specific regulations before they can be imported or exported.
Examples of restricted goods in international shipping include pharmaceuticals and medical devices, alcohol and tobacco, agricultural products and many more.
S
T
Tariffs
Tariffs in international shipping refer to the fees or taxes imposed on goods when transported across international borders. They represent a tax or duty levied by governments and can vary based on factors such as the type of goods, their value, and the trade agreements in place between the countries involved. Each country typically sets its own tariffs, which can differ widely depending on trade policies, economic objectives, and international agreements. Also see Import Duty.
U
V
W
WCO
WCO stands for the World Customs Organization. It is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium, with a mission to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of customs administration worldwide.
The WCO develops international standards and guidelines for customs procedures, promotes cooperation and information sharing among customs authorities, provides technical assistance and capacity support to its members, and facilitates dialogue and collaboration between governments, international organizations, and the private sector on customs-related issues. Their primary objective is to facilitate legitimate trade while ensuring the security and safety of the global supply chain.
X
Y
Z
Unlocking Success: Your Guide to International Shipping Terms
We hope this glossary is a valuable resource in demystifying the intricacies of international shipping terminology. From understanding CN23 forms to navigating Harmonized System (HS) codes, we’ve covered all the essentials needed to succeed in the world of global trade and international shipping terms.
Mastering international shipping terms is not just about deciphering regulations – it’s about unlocking opportunities for growth and expansion in your e-commerce business. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting out, the insights gained from this glossary will serve you well on your journey to international success.
Thank you for joining us on this enlightening exploration of international shipping terms. We wish you continued success and seamless shipping experiences in all your cross-border endeavors!
Ready to take it further? Dive into our in-depth guide on mastering international shipping. Unlock expert tips and strategies to streamline your global operations. Or read more about how Sendcloud can simplify international shipping for your business. Learn how we can help you navigate customs procedures with ease!